Encountering the “Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested operation” error can be a frustrating experience. This error message indicates a problem with Windows Resource Protection (WRP), a crucial system tool designed to safeguard core Windows resources. In this article, we will explore the causes of this error and provide five effective methods to resolve it. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced user, we’ll guide you through each solution step by step.
Understanding Windows Resource Protection (WRP)
Before delving into the solutions, let’s grasp the significance of Windows Resource Protection (WRP). WRP is an integral security feature within the Windows operating system. Its primary function is to shield vital system files from unauthorized modifications or deletions. WRP employs a file permission system to control access to these critical files and continually monitors them for changes.
If WRP detects any unauthorized alterations, it will restore the affected file from a secure backup. This mechanism ensures that Windows always possesses a functional copy of essential files, contributing to system stability and security. WRP plays a vital role in safeguarding against various threats, including malware and ransomware.
Common Causes of the “Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested operation” Error
This error typically arises due to corruption within Windows system files. Several factors can lead to such corruption, including:
- Virus or malware infections.
- Hardware failures.
- Incorrect computer shutdown procedures.
- Corrupt or damaged system files.
- Incorrect file permission settings.
- Issues within the Windows Registry.
- Malware presence on your device.
- A corrupted user profile.
Each underlying cause necessitates a specific approach to resolution. Let’s explore five methods to rectify this error:
Method 1: Run the System File Checker (SFC Scan)
The System File Checker (SFC) is a built-in Windows utility designed to scan for and repair corrupted or damaged system files. To employ this tool:
- Access the search bar by clicking the magnifying glass icon in your taskbar or pressing Windows + S.
- Type “Command Prompt” in the search box. Right-click on it in the search results and select “Run as Administrator” to launch it with administrative privileges.
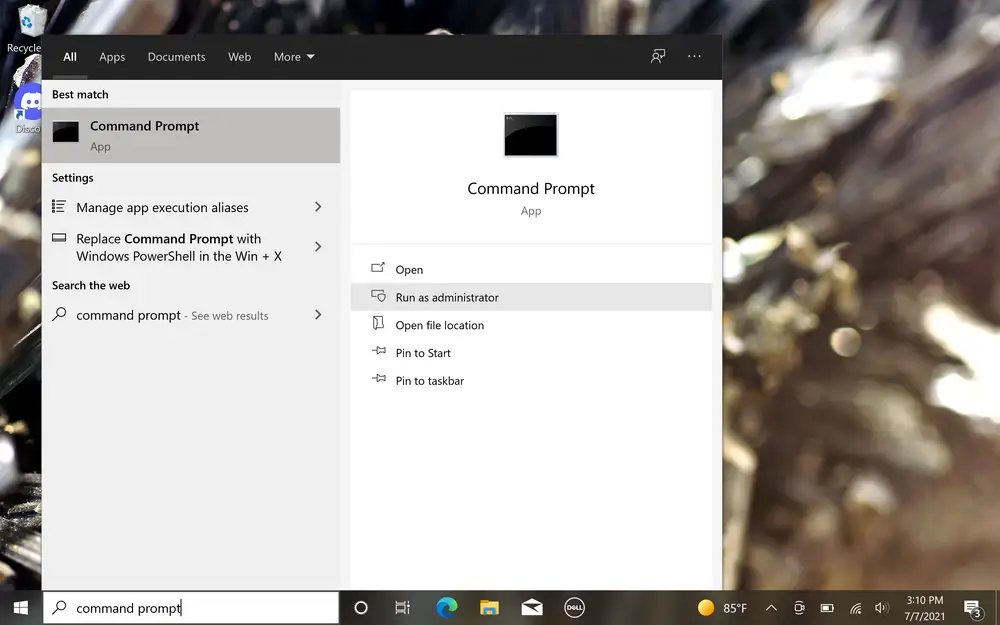
- When prompted by User Account Control (UAC), click “Yes” to grant administrative access.
- Enter the following command and press “Enter”: sfc /scannow
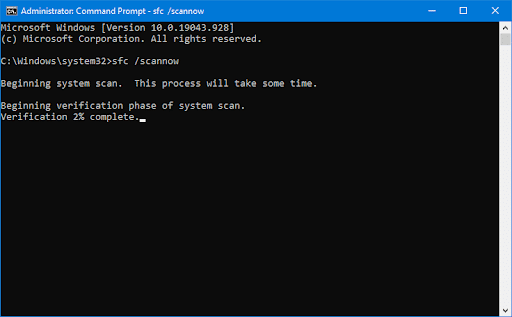
- Allow the System File Checker to complete the scan. Any corrupted system files will be replaced.
Method 2: Utilize the “chkdsk” Command
The “chkdsk” command is a Windows utility that examines your computer’s hard drive for errors, including corrupt files and bad sectors. To utilize this command:
- Open the search bar by clicking the magnifying glass icon in your taskbar or pressing Windows + S.
- Type “Command Prompt” in the search box, right-click on it in the search results, and select “Run as Administrator” to grant administrative access.
- When prompted by UAC, click “Yes.”
- Enter the following command and press “Enter”: chkdsk C: /r
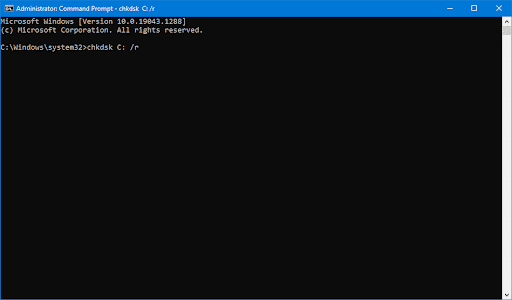
- Wait for the scan to complete.
Method 3: Start the Windows Modules Installer Service
If you’ve disabled the Windows Modules Installer service, the SFC Scan may not function correctly. To enable this service:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run utility.
- Type “services.msc” and click “OK” to open the Services window.
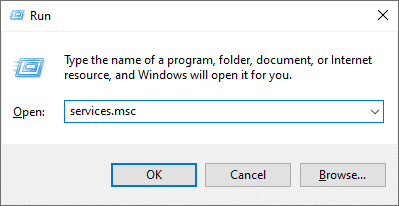
- Right-click on the “Windows Modules Installer” service and select “Properties.”
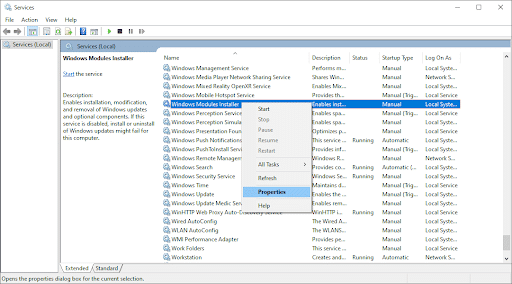
- Set the “Startup type” to “Manual.” If the service isn’t running, click “Start.” Click “Apply” and “OK.”
- Check if the error persists. If so, proceed to the next solution.
Method 4: Run Automatic Repair From Advanced Startup
If previous methods fail, consider running an automatic repair. This built-in tool can resolve various issues with your Windows installation. To initiate the repair:
- Reboot your computer and hold the F8 key (or the Fn key, depending on your device) to access the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
- Select “Troubleshoot” and then “Advanced options.”
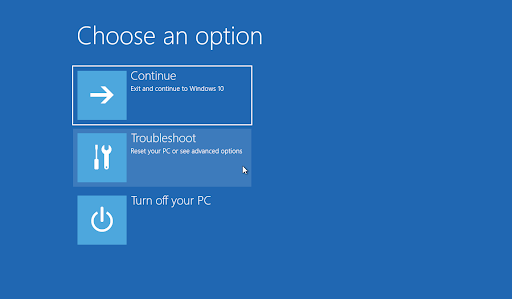
- Click “Startup Repair.” The tool will diagnose and attempt to fix problems affecting Windows’ functionality.
- Follow the on-screen instructions, and provide your local user account details if prompted.
Method 5: Reset or Refresh Windows
If the error persists, resetting Windows may be necessary. This process restores your computer to its default factory settings, resolving software-related issues. Remember to back up your personal files, as they will be deleted during the reset. To reset Windows:
- Click the Start menu, select “Settings,” and type “Reset” into the search bar.
- Click “Reset this PC” from the search results.
- Choose either “Keep my files” or “Remove everything” based on your preference.
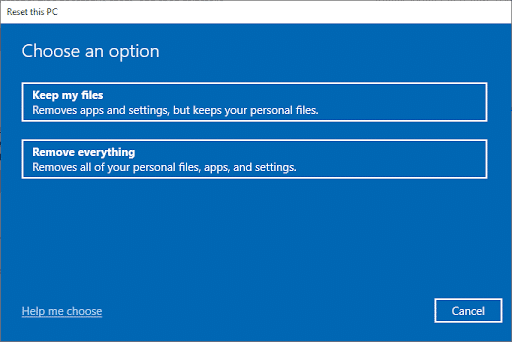
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the reset.
Conclusion
Encountering the “Windows Resource Protection could not perform the requested operation” error can be perplexing, but rest assured that various methods can resolve it. Begin with the System File Checker (SFC) or the “chkdsk” command. If needed, enable the Windows Modules Installer service or run an automatic repair from Advanced Startup. As a last resort, consider resetting Windows. We hope this article has provided valuable insights and guidance for resolving this error effectively. For more tech-related insights and solutions, explore our other blog articles. Thank you for reading, and we trust that this information has been helpful!